شرکت ایلیانویت سازه میبد
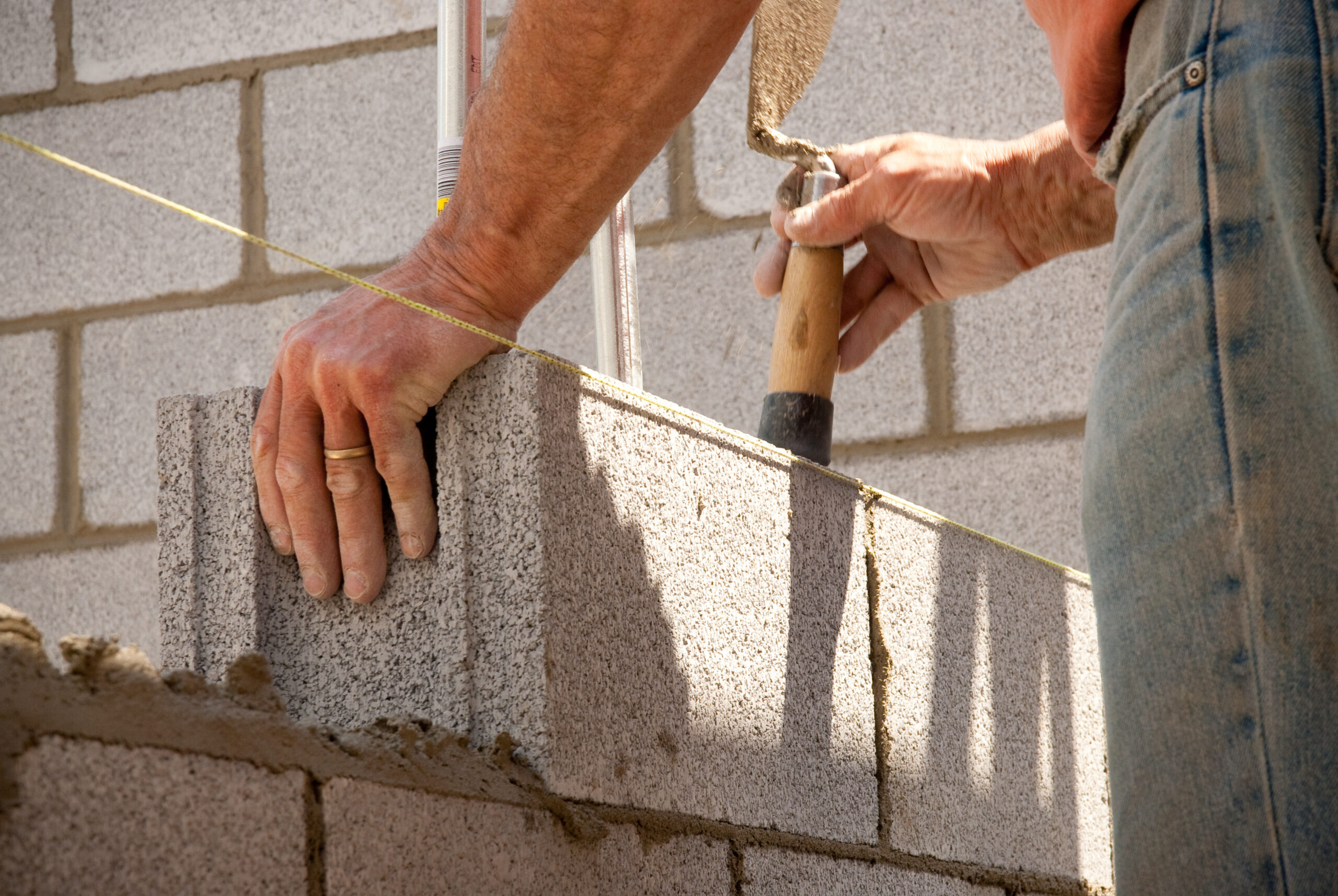
ادامه مطلب- Can masonry mortar be used for wall construction with Ilya blocks?
-
No, it is recommended to use standard adhesive because it reduces the amount of material used and eliminates the thermal bridge in horizontal joints.
- How should corrosion-resistant fiberglass mesh be used on Ilya walls?
-
Two methods can be suggested: • Method 1: Place the fiberglass mesh on a layer of plaster or putty applied to the wall, then press it down by hand until it sinks into the layer. Continue applying plaster or putty until the mesh is completely covered. • Method 2: Use a stapler or hammer to fix the mesh onto the wall, and then cover it with plaster or putty, ensuring the mesh is embedded and can be easily applied over surfaces.
- How much overlap should fiberglass mesh have?
-
Fiberglass mesh should overlap by at least 5 centimeters at the edges. It is important that the mesh maintains this overlap to ensure adequate strength in the vertical direction.
- Does the recommended Ilya mesh have any specific features, or can other meshes be used for reinforcing walls?
-
Meshes should comply with installation instructions, particularly around stress-concentrated areas like columns, openings, and wall posts. Fiberglass mesh should have the necessary tensile strength, which is why Ilya's recommended mesh is used. Plastic meshes available in the market lack sufficient tensile strength.
- Is it possible to replace vertical and horizontal wall posts with fiberglass mesh?
-
According to clause 6-1-4-2-11 of Appendix 6 of the Building Code, when fiberglass mesh is used on both sides of the wall, there is no need to install vertical and horizontal wall posts. This approach eliminates the restriction on the length of walls and allows for greater flexibility in wall design.
- Why should you wait 10 minutes after preparing Ilya's ready-mix adhesive before mixing it again and using it?
-
The 10-minute wait is required to dissolve the polymers in water and activate the adhesive’s properties.
- How are reinforced panels connected to each other?
-
Reinforced panels are connected from the sides using standard Ilya block adhesive and are anchored at the ends using angle iron or channels.
- If Ilya panels are used, is the use of wall posts eliminated?
-
Due to their adequate tensile strength, reinforced panels do not require vertical or horizontal wall posts, as they can be anchored on both sides of the structure.
- What weight should be considered for each square meter of Ilya blocks in design calculations?
-
According to the national building regulations, the dry density of gas concrete is 600 kilograms per cubic meter. The surface weight of the wall, including the finish, is calculated based on this density. For other types of blocks, the weight should be based on the specific density range of 1100 to 1500 kilograms per cubic meter. Designers should use these values to control the overall weight of the structure by referring to the appropriate load tables.
- Can ceramic tiles or tile adhesives be applied directly on the Ilya blocks or their plaster layers?
-
Yes, it is possible to use polymer-modified cement-based tile adhesives (Polymer Modified) to adhere tiles and ceramics directly on plastered surfaces. For optimal results, it is recommended to first apply a primer layer to the plastered surface to enhance water resistance and adhesion, especially since there is a risk of chemical reaction between cement and plaster (ettringite formation: CaSO4+1/2 H2O + cement). Applying a primer prevents potential issues by creating a barrier between the two materials.
- In what dimensions are reinforced Ilya panels produced?
-
Ilya reinforced panels are produced in two types: wall and ceiling panels, with lengths up to 6 meters, widths of 60 centimeters, and thicknesses ranging from 7.5 to 37.5 centimeters, based on customer orders.
- How do AAC Ilya blocks resist rodents and termites?
-
The mineral nature of AAC Ilya blocks and the absence of nutrients prevent the growth and nesting of rodents and termites. These pests are unable to penetrate the solid structure of the blocks, which lacks the cavities or crevices found in other materials that rodents might exploit. Therefore, AAC Ilya blocks are ideal for use in pest-prone environments, offering additional peace of mind to homeowners and builders.
- What is the economic benefit of using Ilya blocks?
-
When constructing a wall with a surface area of 3 square meters (9 cubic meters), using Ilya blocks with a weight of only 522 kilograms can replace traditional blocks or bricks that would weigh around 765 kilograms. This significant reduction in weight not only facilitates faster and easier construction but also reduces transportation costs and handling time. As a result, many recent builders and suppliers prefer using AAC blocks for their projects due to these economic benefits.
- What is the amount of weight reduction achieved in a building constructed with Ilya blocks?
-
The dry density of Ilya blocks ranges between 450 to 500 kilograms per cubic meter, which is about a third of the density of traditional building materials. A 10-centimeter-thick Ilya block wall weighs approximately 58 kilograms per square meter, compared to 108 kilograms for a typical wall made of ordinary blocks. By using Ilya blocks with a thickness of 20, 25, or 30 centimeters, you can achieve a total volume weight reduction of up to 1000 kilograms per square meter, significantly lightening the structural load.
- Which country is the technology used in the production of Ilya blocks from?
-
As you know, the origin of this product is Europe, and currently, European countries, led by Germany, are at the forefront of this industry worldwide. Among the prominent German manufacturers, the renowned HESS company has secured the top position in this industry through innovation and advancements in recent years. HESS has established and supported large factories across the United States, throughout Europe, Russia, and Asia. Ilya Novin Company, by fully purchasing the production line and transferring technical knowledge from HESS Germany, is the only holder of German technology in this industry in Iran.
- What sizes are Ilya blocks produced in?
-
Ilya blocks are produced according to European standards. They are 60 centimeters in length and 25 centimeters in height, with thicknesses ranging from 7.5 centimeters to 37.5 centimeters, depending on customer orders. Special orders with custom sizes, such as heights of 20, 50, and even up to one meter, are also possible
- What are the main differences between autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks and lightweight cement blocks or lightweight aggregate blocks?
-
Firstly, it is important to note that the Iranian national standard for AAC blocks (Standard No. 8593 ISIRI) is directly translated from the European standard (EN-771-4), and all certificates issued by the Standards Organization and the Technical Certificate from the Ministry of Roads and Urban Development are based on this standard. Thus, customers can be assured that they will receive a product that meets European brand standards from a reputable manufacturer. However, for all lightweight cement blocks, which are usually made from any combination of lightweight aggregate and cement, a national standard (No. 7782 INSO) exists. Part of this standard addresses weight according to ASTM C129, while the compression strength and other characteristics seem to be defined based on the preferences of the manufacturers of these blocks (which has led to a reduction from 4 MPa to 2 MPa).
- How are AAC blocks resistant to fire?
-
According to tests conducted by the Ministry of Roads, Housing, and Urban Development's Research Center, based on Iran National Standard No. 1-12055 and European Standard BS EN 1634-1, these blocks, with a minimum thickness of 10 centimeters, offer up to 4 hours of fire resistance. Even after exposure to water, they maintain their integrity. AAC blocks preserve their structure under fire conditions, prevent the spread of flames, and do not emit harmful smoke. For these reasons, AAC blocks are highly recommended for locations requiring superior fire resistance, such as residential buildings, properties, and equipment.
- What role does lime play in the production of autoclaved aerated concrete?
-
Lime undergoes a grinding process to reach a specific fineness (measured in Blaine, similar to cement) and then mixes with cement and gypsum. The resulting mix of lime and cement forms a calcium silicate gel that contributes significantly to the final product's structure. Lime reacts with water in this phase, allowing the aluminum powder to generate hydrogen gas. The released hydrogen creates a porous structure by expanding within the concrete mixture, making it lightweight. However, in the later stages of production, lime contributes to the formation of calcium hydrosilicates, which remain part of the final block structure after the autoclaving process.
- Is autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) a new product?
-
Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) was developed in Europe more than 80 years ago and has been widely used for over 40 years in Europe, the USA, and Australia. It first appeared in America about 20 years ago, and its application continues to expand globally. In current markets, AAC blocks are available in various dimensions and densities, ranging from 75 to 650 kilograms per cubic meter. They are produced under stringent quality control conditions, making them a reliable choice for both construction and renovation projects. Despite the challenges faced by manufacturers, AAC remains one of the most advanced and energy-efficient building materials available today, particularly for improving the seismic performance of buildings. In summary, the benefits of AAC blocks, including their structural integrity, fire resistance, and energy-saving properties, make them a preferred choice for modern construction projects over traditional building materials.
- What is the difference between AAC blocks and non-autoclaved (foam concrete) blocks?
-
The autoclaving process, which occurs at about 190 degrees Celsius under pressure for 12 hours, results in minimal shrinkage and creates a stable structure within AAC blocks. During this process, calcium hydrosilicates form, and the autoclave transforms the blocks into a stable and strong material. In contrast, foam concrete, which undergoes long drying and hardening periods, often experiences significant shrinkage and cracking. One key difference is that foam concrete typically has a higher density and less stability, which can lead to weight gain rather than the weight reduction benefits provided by AAC blocks.
- Do AAC blocks absorb moisture?
-
AAC blocks, unlike other building materials, do not absorb moisture deeply, only up to a depth of3.5 centimeters. While some changes in color might occur due to surface absorption, these changes do not penetrate deeply and do not affect the block's structure. AAC blocks are designed to prevent moisture from penetrating beyond their surface, thus preserving their integrity. They resist moisture, keeping walls and roofs protected from the adverse effects of prolonged exposure to water.
- In which sectors are autoclaved aerated concrete blocks used?
-
Autoclaved aerated concrete blocks are widely used around the world, especially in hospitals, hotels, restaurants, shops, warehouses, office buildings, cultural and educational institutions like libraries and schools, and hospitals and universities.
- What is the method for installing mechanical and electrical utilities in walls made with AAC blocks?
-
AAC blocks have properties similar to wood in terms of workability; they can be easily cut, drilled, or grooved using common commercial tools. Grooves for mechanical and electrical installations can be easily created on the block surfaces without breaking them, and utilities can be installed in these grooves without the need for extensive repairs. For larger installations or specific construction needs, cementitious or other suitable materials can be used to secure the utilities. This property significantly simplifies the installation of mechanical and electrical systems compared to conventional methods.
- Why is autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) suitable as a thermal insulator?
-
Due to its design and material properties, AAC has significant effects on energy consumption and heat transfer, especially in commercial and residential buildings. It reduces energy loss through walls, roofs, and floors. The closed cell structure of AAC blocks provides excellent thermal insulation, which helps keep interiors warm in winter and cool in summer. This not only reduces heating and cooling costs but also contributes to improving living conditions and working environments. Moreover, it aligns with energy-saving policies and is environmentally friendly.
- Can a plaster finish be applied directly to AAC blocks to create a smooth surface?
-
Yes, using a thin layer of plaster (0.5 to 1 centimeter thick) will result in a smooth surface suitable for painting. If properly applied, this method provides a clean, level surface ready for any finishing material, such as paint or wallpaper.
- Are AAC blocks load-bearing?
-
Yes, AAC blocks produced by this company, with a density of 500 kilograms per cubic meter, have an average compressive strength of over 2 MPa, with maximum strengths reaching up to 4 MPa. These blocks meet the standards for structural load-bearing applications in walls, offering adequate support for residential and commercial construction needs. With permissible stress under load up to 0.375 MPa and a safety factor of 2.5, they are suitable for constructing load-bearing walls.
For questions and more information, contact the number below.
035-32372929